Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
컴퓨터는 잘못이 없다..
[JAVA]변수와 자료형 본문
Contents
접기
#핵심요약
- 변수는 이름짓는 규칙이 존재한다.
- 문자, 숫자, _, $ 가능
- 숫자로 시작 x, 공백사용 x, 예약어사용 x
- 변수의 특징
- 대소문자 구분
- 변수는 이름짓는 규칙이 존재한다.
- 변수, 함수는 카멜표기법, class명은 파스칼표기법으로 표기한다.
- 자료형 종류
- 정수, 실수, 부울, 문자, 문자열
- StringBuffer, List, Map 등이 있다.
- StringBuffer은 문자를 자주 변경할 때 사용한다.
- 변경이 자주 일어나도 객체는 딱 한번만 생성된다.
- equals와 ==의 차이점?
- equals는 값을 비교 ==는 객체를 비교한다.
#소스코드
변수와 자료형_1
// Java 프로그래밍 - 변수와 자료형_1
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 변수 사용하기
System.out.println("== 변수 사용하기 ==");
int age = 10;
String country = "Korea";
System.out.println("age = " + age);
System.out.println("country = " + country);
System.out.println();
// 2. 변수 이름 규칙
System.out.println("== 변수 이름 규칙 ==");
// 2-1. 문자, 숫자, _(underscore), $ 사용 가능
int apple = 2000;
int apple3 = 2000;
int _apple = 2000;
int $apple = 2000;
System.out.println("apple = " + apple);
System.out.println("apple3 = " + apple3);
System.out.println("_apple = " + _apple);
System.out.println("$apple = " + $apple);
System.out.println();
// 2-2. 숫자로 시작 X
// int 3apple = 2000;
// 2-3. 대소문자 구분
int apple1 = 2000;
int Apple1 = 3000;
System.out.println("apple1 = " + apple1);
System.out.println("Apple1 = " + Apple1);
System.out.println();
// 2-4. 공백 사용 X
// int one apple = 2000;
int one_apple = 2000;
int oneApple = 2000;
// 2-5. 예약어 사용 X
// 예약어 예시: true, false, if, switch, for, continue, break, ...
// int true = 1;
// int false = 0;
// int if = 1;
// int continue = 10;
// 참고) 한글 사용 가능
int 나이 = 20;
System.out.println("나이 = " + 나이);
// 3. 표기법
System.out.println("== 표기법 ==");
// 3-1. 카멜 표기법 (camelCase)
// 변수, 함수
int myAge = 10;
int oneApplePrice = 1000;
// 3-2. 파스칼 표기법 (PascalCase)
// 클래스 ex. public class Main <- 클래스 이름 Main
int MyAge = 10;
int OneApplePrice = 1000;
// 참고) 스네이크 표기법 (snake_case)
// 사용 X
int my_age = 10;
int one_apple_price = 1000;
}
}
변수와 자료형_2
// Java 프로그래밍 - 변수와 자료형_2
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 자료형 - 숫자
System.out.println("== 숫자 ==");
// 1-1. 정수
int intNum = 10;
System.out.println("intNum = " + intNum);
System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
int intNum2 = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int intNum3 = Integer.MAX_VALUE + 1; //잘못된 값이 들어가게 된다.
System.out.println("intNum3 = " + intNum3);
long longNum = (long)Integer.MAX_VALUE + 1; //Integer타입에 들어가는 값보다 더 많은 값을 넣을때는 long타입에 넣어준다.
System.out.println("longNum = " + longNum);
// 1-2. 실수
float floatNum = 1.123f;
System.out.println(Float.MAX_VALUE);
double doubleNum = 3.4028;
System.out.println(Double.MAX_VALUE);
// 1-3. 2진수 / 8진수 / 16진수
int numBase2 = 0b1100;
int numBase8 = 014;
int numBase16 = 0xC;
System.out.println(numBase2);
System.out.println(numBase8);
System.out.println(numBase16);
System.out.println("0b" + Integer.toBinaryString(numBase2));
System.out.println("0" + Integer.toOctalString(numBase8));
System.out.println("0x" + Integer.toHexString(numBase16));
// 2. 자료형 - 부울
System.out.println("== 부울 ==");
boolean isPass = true;
boolean isOk = false;
System.out.println(isPass);
System.out.println(isOk);
// 3. 자료형 - 문자
System.out.println("== 문자 ==");
char keyFirst = 'a';
char keyLast = 'z';
System.out.println(keyFirst);
//int형으로 변환하면 숫자로 출력된다.
//이는 각 문자들이 아스키코드로 매핑되어있는 것을 의미한다.
System.out.println((int)keyFirst);
System.out.println((int)keyLast);
}
}
변수와 자료형_3
// Java 프로그래밍 - 변수와 자료형_3
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 자료형 - 문자열
System.out.println("== 문자열 ==");
String s1 = "Hello World!";
String s2 = "01234";
System.out.println("s1 = " + s1);
System.out.println("s2 = " + s2);
// 1-1. equals
String s3 = "hi";
String s4 = "hi";
System.out.println(s3.equals(s4)); //true
System.out.println(s3 == s4); //true
String s5 = new String("hi");
System.out.println(s3.equals(s5)); //true -> 값을 비교
System.out.println(s3 == s5);//false -> 객체를 비교
// 1-2. indexOf : 특장 문자열의 위치를 알려주는 메소드 (0부터 시작)
String s6 = "Hello! World!";
System.out.println(s6.indexOf("!")); //5
System.out.println(s6.indexOf("!", s6.indexOf("!") + 1)); //12 두번째 느낌표의 위치를 찾아주는 방법
// 1-3. replace
String s7 = s6.replace("Hello", "Bye");
System.out.println("s7 = " + s7);
// 1-4. substring
System.out.println(s7.substring(0, 3)); //Bye
System.out.println(s7.substring(0, s7.indexOf("!") + 1)); //Bye!
// 1-5. toUpperCase
System.out.println(s7.toUpperCase()); //BYE! WORLD!
// 2. 자료형 - StringBuffer
System.out.println("== StringBuffer ==");
StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer(); //많이 변경해도 sb1 (객체) 이 새로 생겨나지 않는다.
sb1.append("01234");
System.out.println("sb1 = " + sb1);
sb1.append("56789");
System.out.println("sb1 = " + sb1);
String a = "01234";
String b = "56789";
String bak = a;
System.out.println(a == bak); //true 1. a에 변경이 없었을 땐 같은 객체였다가
a += b; //2. 변경할 때마다 객체를 새로 생성한다. 즉, a객체를 새로 생성함
System.out.println(a == bak); //false 3. 그래서 a와 bak은 다른 객체라고 나온다.
//즉, append로 문자열을 붙이나, +=으로 붙이나 결과는 같지만
//StringBuffer을 통해 append로 문자열을 붙이면 객체가 새로 생겨나지 않고
//+=으로 문자열을 붙이면 붙일 때마다 객체가 새로 생겨난다.
// StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer("name is");
// sb2.insert(0, "My ");
// sb2.insert(sb2.length(), " JAVA");
// System.out.println("sb2 = " + sb2);
// System.out.println(sb2.substring(0, 2));
// 3. 자료형 - 배열
System.out.println("== 배열 ==");
int[] myArray1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
System.out.println(myArray1[0]);
System.out.println(myArray1[1]);
System.out.println(myArray1[2]);
System.out.println(myArray1[3]);
System.out.println(myArray1[4]);
char[] myArray2 = {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'};
System.out.println(myArray2[2]);
String[] myArray3 = new String[3];
myArray3[0] = "Hello";
myArray3[1] = " ";
myArray3[2] = "World!";
System.out.println(myArray3[0] + myArray3[1] + myArray3[2]);
}
}
1-1. equals 에 대한 부가설명
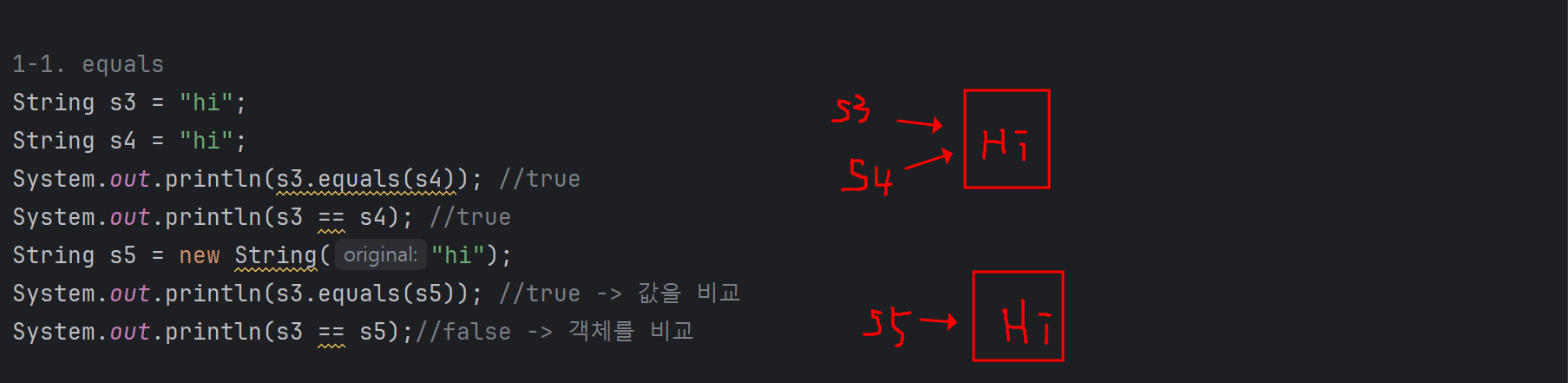
String 타입을 어떻게 생성하느냐에 따라 차이가 있다. equals는 값을 비교, ==는 객체를 비교한다.
변수와 자료형_4
// Java 프로그래밍 - 변수와 자료형_4
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 자료형 - 리스트
System.out.println("== 리스트 ==");
ArrayList l1 = new ArrayList(); //import 해야함
// 1-1. add
l1.add(2);
l1.add("hello");
l1.add(3);
l1.add(4);
l1.add("world");
System.out.println("l1 = " + l1);
l1.add(0, 1);
System.out.println("l1 = " + l1);
// 1-2. get
System.out.println(l1.get(0));
System.out.println(l1.get(1));
// 1-3. size
System.out.println(l1.size());
// 1-4. remove
l1.remove(1); //index를 넣어줘야 함
System.out.println("l1 = " + l1);
l1.remove(Integer.valueOf(1)); //해당 값을 지울 때 사용
System.out.println("l1 = " + l1);
l1.remove("hello");
System.out.println("l1 = " + l1);
// 1-5. clear : list를 비워줌
l1.clear();
System.out.println("l1 = " + l1);
// 1-6. sort
ArrayList l2 = new ArrayList();
l2.add(5);
l2.add(3);
l2.add(4);
System.out.println("l2 = " + l2); //l2 = [5, 3, 4]
l2.sort(Comparator.naturalOrder()); //오름차순 정렬
System.out.println("l2 = " + l2); //l2 = [3, 4, 5]
l2.sort(Comparator.reverseOrder()); //내림차순 정렬
System.out.println("l2 = " + l2); //l2 = [5, 4, 3]
// 1-7. contains
System.out.println(l2.contains(1)); //해당 데이터가 있는 지 확인
System.out.println(l2.contains(3));
// 2. Maps : key와 value
System.out.println("== Maps ==");
HashMap map = new HashMap();
// 2-1. put
map.put("kiwi", 9000);
map.put("apple", 10000);
map.put("mango", 12000);
System.out.println("map = " + map);
// 2-2. get
System.out.println(map.get("mandarin"));
System.out.println(map.get("apple"));
// 2-3. size
System.out.println(map.size());
// 2-4. remove
System.out.println(map.remove("hi")); //없는 걸 지우고 출력시키면 null 츌력
System.out.println(map.remove("mango")); //있는 걸 지우고 출력시키면 키에 매핑된 value값 출력
System.out.println("map = " + map);
// 2-5. containsKey : 해당 키가 있는지 없는 지 검사
System.out.println(map.containsKey("mango"));
System.out.println(map.containsKey("kiwi"));
// 3. Generics : 지정된 타입의 데이터만 넣을 수 있음
System.out.println("== Generics ==");
ArrayList l3 = new ArrayList();
l3.add(1);
l3.add("hello");
System.out.println("l3 = " + l3);
ArrayList<String> l4 = new ArrayList<String>();
// l4.add(1);
l4.add("hello");
HashMap map2 = new HashMap();
map2.put(123, "id");
map2.put("apple", 10000);
System.out.println("map2 = " + map2); //map2 = {apple=10000, 123=id}
HashMap<String, Integer> map3 = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
// map3.put(123, "id");
map3.put("apple", 10000);
System.out.println("map3 = " + map3); //map3 = {apple=10000}
}
}
'공부 > JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA]여러가지 연산자 (1) | 2024.04.07 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA]InnerClass3_퀴즈_Inner Class 객체 생성하기 (0) | 2020.12.29 |
| [JAVA]InnerClass2_Inner Class에서 this의 사용 (0) | 2020.12.29 |
Comments


